TERMS AND DEFINITIONS
ASYMMETRIC ENCRYPTION
Asymmetric encryption uses distinct keys and algorithms for encryption and decryption. Public private key encryption uses asymmetric encryption. Also see the definitions of
private and public keys.
CERTIFICATE
A computer-generated record that ties the user's identification with the user's public key in a trusted bond. The trust is based on registration/identification policy enforced by a third party, Certification Authority. The certificate contains the following: identification of the Certification Authority issuing the certification; the user; the user's public key; and is digitally signed by the issuing Certification Authority.
CERTIFICATION AUTHORITY
An individual trusted and empowered to create and sign Certificates. CA certifies user's identity and association with key. This is at the "lowest level" in the certification hierarchy. Using physical CA servers, the CA will manage user certificates (information about the DOD member) and corresponding public keys. This consists of building Certificate Revocation Lists to directories, and user management processes such as certificate renewal.
CERTIFICATION HIERARCHY
CAs are subordinate to a Root-CA (and possibly more than one or more intermediate CAs). The nature of the subordination is described in one or more Certification Practice Statements (CPS) [generated for that hierarchy], and implemented through procedure and certificate extensions.
[CP]
CERTIFICATE POLICY (CP)
A named set of rules that indicates the applicability of a certificate to a particular community and/or class of application with common security requirements. For example, a particular CP might indicate applicability of a type of certificate to the authentication of parties engaging in business-to-business transactions for the trading of goods or services within a given price range.
CERTIFICATION PRACTICES STATEMENT (CPS)
A statement of the practices that a certification authority employs in issuing, managing, revoking, and renewing or re-keying certificates. The Certification Practice Statement establishes the proofing requirements for identifying the private key owner that must be satisfied before creating a certificate. There is a wide range of options for how robust (and resource intensive) this proof must be. The Certification Authority employs these procedures when issuing certificates, the clarification of parties' legal rights and obligations.
CERTIFICATE REVOCATION LIST
A computer generated record that identifies certificates that have been revoked or suspended prior to their expiration dates. It is periodically issued by each certification authority and posted to the directory.
[RM]
COMMON USER INTERFACE (CUI)
An interface facilitating human interaction with computer systems.
Top of Page
DIGITAL SIGNATURE
A digital signature is an electronic analogue of a written signature in that the digital signature can be used in proving to the recipient or a third part that the message was, in fact, signed by the originator.
DIGITAL SIGNATURE STANDARD (FIPS 186)
This standard specifies a Digital Signature Algorithm appropriate for applications requiring a digital rather than written signature.
DIRECTORY
The directory provides a repository from which users can obtain public key certificates for themselves and for other users and where they can verify that certificates have not been revoked. User's public key certificates are stored in the directory. Responsibilities of the directory include:
- Receiving and storing certificates and CRLs sent from the Root CAs.
- Maintaining appropriate indexes to provide efficient search and retrieval of CRLs and certificates by users.
- Providing highly reliable, full-time availability to directory information.
- Submitting expired certificates and CRLs to an archive.
DIRECTORY SERVER (DS)
This is a physical database that stores information and key materials for each DOD member active (or allowed to be active) in the system. It also stores a Certificate Revocation List (CRL), to allow persons in the hierarchy and other DOD members to determine if a particular certificate/member is still valid.
DISTINGUISHED NAME
A unique identifier used to locate a person in a directory and obtain their public key information.
ENCRYPTION
Transforming a text into code in order to conceal its meaning. The process of transforming data to an unintelligible form in such a way that the original data either cannot be obtained (one-way encryption) or cannot be obtained without using the inverse decryption process.
Top of Page
FIXED KEY STORAGE
A user's fixed storage (e.g., hard drive) is the least secure. The keys are typically protected by password-based encryption, but still are susceptible to snooping and remote penetration. It is generally far easier to break the password protection than to decrypt a message protected by the key.
FORTEZZA CARD
The FORTEZZA card is a cryptographic peripheral that provides encryption/decryption and digital signature functions. It also stores "certificates" which include individualized key material used by the cryptographic and signature functions.
HASH FUNCTION
A hash function is used in the signature generation process to obtain a condensed version of the data, called a message digest. The message digest is then input to the Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) to generate the digital signature. The same function must also be used in the verification process. The hash function is specified in FIPS 180-1, Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA-1).
[FIPS 180-1]
KEY PAIR
The key pair consists of corresponding public and private keys. The two keys generated at the same time. Public key cryptography provides a simple means for creating secure, authenticated messages. In a public key system (also know as asymmetric) two keys are generated for a user. One of these keys is kept private and is hence termed their private key. The other key is widely published and is termed their public key. This technology lends itself to providing the following security services:
- private communication - user A wishing to talk privately to user B encrypts messages using the public key of B. This message can then only be decrypted by B.
- digital signatures - user A can digitally sign a document by encrypting a unique digest of the message with their private key. The source of this document can then be verified by decrypting the signature with the users public key and comparing it to the digest of the message (Figure 1).
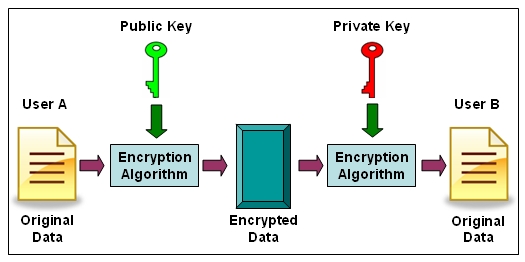
Figure 1. Key Pair
LIGHTWEIGHT DIRECTORY ACCESS PROTOCOL (LDAP)
An internet protocol that email and other programs use to look up information from a server. The LDAP protocol is also used to look up the status of encryption certificates.
LOCAL REGISTRATION AUTHORITY (LRA)
The local, (onsite) point of contact that provides the user with their password and unique ID. The LRA provides this information to the Certification Authority (CA). The LRA is the location on the post, camp, or station where information about user's transfer, death, name change, etc. is collected and then relayed to the CA.
Top of Page
NAMING AUTHORITY (NA)
Responsible for establishing the naming structure used in a domain and ensuring uniqueness of names. Although in theory, a NA could supply distinguished names for all users, in practice, the task is typically delegated to registration authorities. The NA is responsible for developing a scheme to ensure uniqueness.
PRIVATE AND PUBLIC KEY
There is a growing demand to be able to perform transactions via the network rather than via traditional paper-document methods. Activities such as command and control, official release of procurement documents, and travel reimbursement approvals are accompanied by legal requirements for non-repudiation. The DOD intends to satisfy these legal requirements for non-repudiation by deploying digital signature and signature verification mechanisms. Closely related to digital signatures is authentication. One way that 'A' can authenticate 'B's' identity, if they know A's public key, is by having A sign a challenge. If the signature can be verified with A's public key, A must have signed it. Private and public keys correspond to each other, but differ. The pair of keys provides public key cryptography functions. Each user possesses a private and public key pair.
PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE
The framework and services that provide for the generation, production, distribution, control and accounting of public key certificates; a system with multiple components coupled with management which provides security services. The initial PKI system will allow DOD members to register for and obtain digital encryption and signature keys. This will ensure the following services over the DII at a reasonably high level of assurance (trust of information):
- Authentication: Proof that the sender is whom he claims to be. (public/private key)
- Non-repudiation: Assurance that the person sending cannot deny participation. (digital signature)
- Integrity: Verification that no unauthorized modification of data has occurred. (hash)
- Confidentiality: Assurance that the person receiving is the intended recipient. (encrypt/decrypt)
REGISTRATION AUTHORITY
A Registration Authority is an official recognized by the certification authority to ensure that the subscriber's appropriately present the necessary credentials for registration into the PKI. In the DoD PKI, RAs enroll devices into the PKI, revoke user certificates and authorize the LRAs to enroll individual subscribers.
RELYING PARTY
Relying parties are people or organizations that rely on information in a certificate and the integrity of the PKI to make decisions, make resources available to the users, or accept instructions from the users. Responsibilities of a relying party include:
- Verifying the certificate is valid.
- Ensuring the certificate has not been revoked.
- Relying on certificates only to the extent permitted by policy.
REMOVABLE KEY STORAGE
Removable storage, such as a diskette, is less secure, but still has the advantage of being portable and can be kept in a physically secure container when not being used. The advantage is that the keys are not constantly available on the machine for snooping, etc.
ROOT CERTIFICATION AUTHORITY
The Root CA is a trusted entity responsible for establishing and managing a PKI domain by issuing CA certificates to entities authorized and trusted to perform CA functions.
[RM]
Top of Page
TOKEN
NIST defines a token as "Something that the claimant possesses and controls (typically a key or password) used to authenticate the claimant's identity." Private keys associated with certificates are stored in tokens, which can either be software or hardware based. Software tokens for private keys are typically stored on workstations within applications. Hardware tokens are smart cards or other devices used to generate, store, and protect cryptographic information, and can themselves perform cryptographic functions.
[FAQ]
X.500 DIRECTORY SERVICE
The X.500 Directory Service is a "whitepage" directory service that maintains specific information about people including names, email addresses, and other pertinent information on network directory servers. The model for directory service is based on a global directory model called LDAP, which stands for the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol. LDAP is a directory service protocol that runs over TCP/IP. The details of LDAP are defined in RFC 1777 "The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol."
X.509 CERTIFICATE
The certificate is the International Telecommunications Union - Telecommunication Standardization Section (ITU-T) recommendation that defines a framework for the provision of authentication services under a central control paradigm represented by a "Directory". The recommendation describes two levels: simple authentication, using a password as verification of claimed identity, and strong authentication, involving credentials formed by using cryptographic techniques, the "certificate". The format of the certificate structure is defined along with responsibilities of the Certification Authority in regards to establishing and maintaining trust.
LEGAND (SOURCE OF DEINITIONS):
CP=DOD X.509 CERTIFICATE POLICY
FAQ=DOD PKI AND PUBLIC KEY ENABLING FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
FIPS 186=FEDERAL INFORMATION PROCESSING STANDARD - DIGITAL SIGNATURE STANDARD (DSS)
FIPS 180-1=FEDERAL INFORMATION PROCESSING STANDARD - SECURE HASH ALGORITHM, MODIFICATION 1 (SHA-1)
LRA UG=DOD PKI LOCAL REGISTRATION AUTHORITY USERS GUIDE
RM=DOD PKI ROADMAP
Top of Page